Abstract
Background:
Bendamustine and rituximab (BR) has been a preferred regimen for frontline therapy of patients (pts) with advanced stage follicular lymphoma (FL) since randomized trials demonstrated both favorable efficacy and toxicity profiles (Rummel et al 2013, Flinn et al 2014). However, the incidence of transformation and outcomes of pts with early progression within 24 months (POD24) after BR remain poorly documented. Since 2013, BR has been the recommended frontline therapy for all pts with advanced stage, symptomatic FL in British Columbia (BC). We report this population-based analysis evaluating outcomes following the introduction of BR, including the incidence of transformation and POD24, compared to a historical cohort of pts treated with frontline RCVP.
Methods:
The BC Lymphoid Cancer Database was used to identify all FL pts treated with frontline BR prior to April 1st 2018. A period of observation prior to systemic therapy was permitted, but pts were excluded if they received prior radiation or single-agent rituximab. All pts had pathologically confirmed FL grades 1-3A and symptomatic advanced stage disease (Ann-Arbor I/II if too bulky/not amenable to radiation or stage III-IV). Pts were excluded if they were HIV positive or had documented discordant/composite lymphoma. Event-free survival (EFS), overall survival (OS), and time-to-transformation (TTTF) were calculated from the date of initiation of systemic therapy. Early progression (POD24) was defined as relapse or progression, death from lymphoma or treatment toxicity within 24 months of initiation of systemic therapy. Outcomes were compared with a historical cohort of pts treated with frontline RCVP, which was the recommended induction prior to BR. All pts were eligible to receive rituximab maintenance, which is standard of care for responding pts post-induction therapy in BC.
Results:
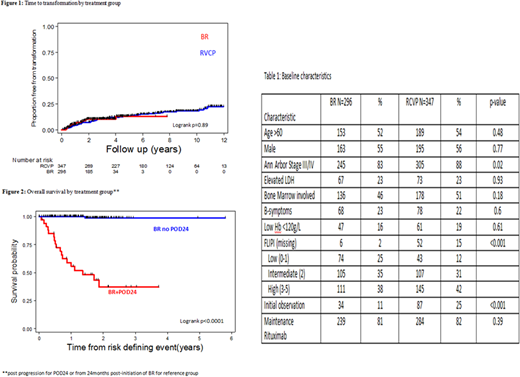
A total of 296 BR-treated pts were identified with a median age of 61 years (range 24-86) and baseline characteristics as outlined in Table 1. Only 34 (11%) had been previously observed and 239 (81%) received rituximab maintenance. A historical cohort of 347 RCVP-treated pts was identified, with comparable clinical characteristics but longer duration of follow-up (median 8.4y, range 0.6-12.6).
With a median follow-up for living pts of 2.8y (range 0.2-7.6), estimates for 2-y EFS and OS were 85% (95% CI 80-89%) and 92% (95% CI 88-95%), respectively, for BR-treated pts. As expected, use of BR was associated with an improvement in EFS compared with RCVP (2-y EFS 76% [95% CI 71-80%], p=0.001), but no difference in OS with current follow-up.
A total of 28 (9%) transformations have occurred in BR-treated pts, 68% of which were documented histologically. Only elevated LDH was associated with increased risk of transformation (p<0.001). Compared with RCVP-treated pts, the incidence of transformation over time appears similar with current follow-up (Figure 1). Post-transformation outcome in BR-treated pts was poor, with 2-y OS 39% (95% CI 18-59).
Early progression (POD24) has occurred in 35/296 (12%) of BR-treated pts. The majority of these, 27 (77%), had transformed lymphoma. Five POD24 pts (14%) died of lymphoma or treatment toxicity without documented transformation and 3 (9%) had relapse with FL and are still alive at last follow up. By comparison, POD24 occurred in 77/347 (22%) of RCVP-treated pts: comprising 31 (40%) transformed lymphoma, 27 (35%) died of lymphoma or treatment toxicity without documented transformation and 19 (25%) relapsed with FL and are still alive at last follow up. Outcome in BR-treated pts with POD24 was poor, with post-progression 2y OS 38% (95% CI 20-55%) compared to non-POD24 BR-treated patients (Figure 2).
Conclusion:
This population-based analysis demonstrates that in the absence of transformation or POD24, pts with advanced stage FL have excellent outcomes after frontline BR. The use of BR has not changed the rate of transformation compared with that seen after frontline RCVP, with limited follow-up. The occurrence of early progression (POD24) may be decreasing following the introduction of BR, but the majority of POD24 pts now have transformed lymphoma. As a consequence, only a small proportion of POD24 pts following BR have FL-only relapse that may be considered for novel approaches specific for FL. A greater impact on outcome for POD24 pts after BR will require early prediction and improved treatment of transformed lymphoma.
Freeman:Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria. Scott:NanoString: Patents & Royalties: Named Inventor on a patent licensed to NanoString Technologies, Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Research Funding. Connors:Merck: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Bristol Myers-Squibb: Research Funding; Cephalon: Research Funding; NanoString Technologies: Patents & Royalties: Named Inventor on a patent licensed to NanoString Technologies, Research Funding; Bayer Healthcare: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Lilly: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria, Research Funding; F Hoffmann-La Roche: Research Funding; Roche Canada: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding. Sehn:Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria; Morphosys: Consultancy, Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria; Lundbeck: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal